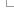Ensembl Regulatory Annotation
The results of peak calling are used to identify potential regulatory regions in the genome, including Promoters, Enhancers and Open Chromatin regions.
Overview of the annotation process
The steps used for defining the set of Regulatory Features (RFs) are:
- Retrieve ATAC-seq & DNase-seq peaks for all the epigenomes of the target species, restricted to the peaks of canonical chromosomes.
- Merge peaks across epigenomes overlapping by at least 1 bp to obtain a set of unique peaks (UPs).
Promoters
- Identify UPs overlapping Transcription Start Site (TSS) windows, defined as 90 bp upstream and 10 bp downstream of a TSS.
- For each UP overlapping a TSS window:
- Merge core regions (490 bp upstream and 10 bp downstream of each TSS) for all TSSs overlapping the UP
- Each merged core region (there can be more than one per UP) becomes the core region of a promoter. A promoter can have longer bounds, which are determined by the overlapping UP, but limited to 10bp downstream of the farthest TSS in the merged core region and 1 kb upstream of the core region.
- The remainder of the UP becomes a candidate open chromatin region (cOCRS).
Open chromatin regions
- Join the cOCRs and the UPs that did not overlap a TSS, merge nearby peaks (up to 100 bp), and filter out peaks shorter than 100 bp. This gives the set of open chromatin regions. A subset of these will be relabelled as enhancers.
Enhancers
- For H3K4me1, H3K27ac and open chromatin peaks (ATAC-seq or DNase-seq), merge nearby peaks (up to 100 bp) across epigenomes to give unique peaks (UPs). Filter out the histone UPs that don’t overlap open chromatin UPs by at least 50% in either direction.
- Filter out open chromatin regions > 2.5 kb or that overlap annotated exons by more than 10%.
- Those that overlap with the H3K4me1 or H3K427ac UPs by more than 50% are relabelled as enhancers.
Activity
- Activity (ACTIVE or INACTIVE) is determined by overlapping features and the epigenome open chromatin peaks when there is:
- For open chromatin regions and enhancers, a minimum of 20% overlap in either direction.
- For promoters, at least 1 bp overlap.